Slang is primarily used within informal conversations and not widely-used within written work. Each person demonstrates different habits when it comes to the way slang is used, with some people using it as common language and others refusing to use it at all.
- One study found that we view others as nicer, smarter, more likable, more professional and more trustworthy when they use proper language over slang in a written message.
- 80% of Americans say that they use slang, with 20% doing so in every conversation.
- Interestingly, 1 in 2 Americans have used slang terms without knowing their meaning.
- When it comes to a professional setting, more than half of people (56%) would not hire a person that uses slang in an interview.
- Furthermore, using slang incorrectly was not a concern for 46% of the respondents.
- 54% admit to worrying about the incorrect use of slang.
- 83% of respondents admit using the internet to find out the meaning of slang terms.
- Slightly lower, 68% of respondents have checked the definition of slang with younger people.
- Whereas 66% of parents mention becoming annoyed by slang, just 46% of non-parents felt the same.
- Slang can even have an impact on romance, with 63% believing it to be a dealbreaker on first dates.
How slang terms are learned
The introduction of new technologies and in particular social media has made it easier for people to create and share new slang terminology. Prior to this, slang typically relied on in-person conversations and visual entertainment such as television and movies to spread.
| Source | Percentage |
| Internet or social media | 28% |
| From friends | 28% |
| From family | 25% |
| From a partner | 11% |
| From entertainment | 7% |
| Other | 1% |
A graph is given below to show how slang terms are learned:

How often slang terms are used
The frequency at which people use slang shows great variation, as we attempt to strike a balance between the different types of language we utilize. However its popularity is still strong, with only a small percentage of people reporting rarely ever using the informal language type.
| Frequency | Percentage |
| Some conversations | 38% |
| Most conversations | 30% |
| Every conversation | 22% |
| Rarely | 10% |
A graph is given below to show how often slang terms are used:

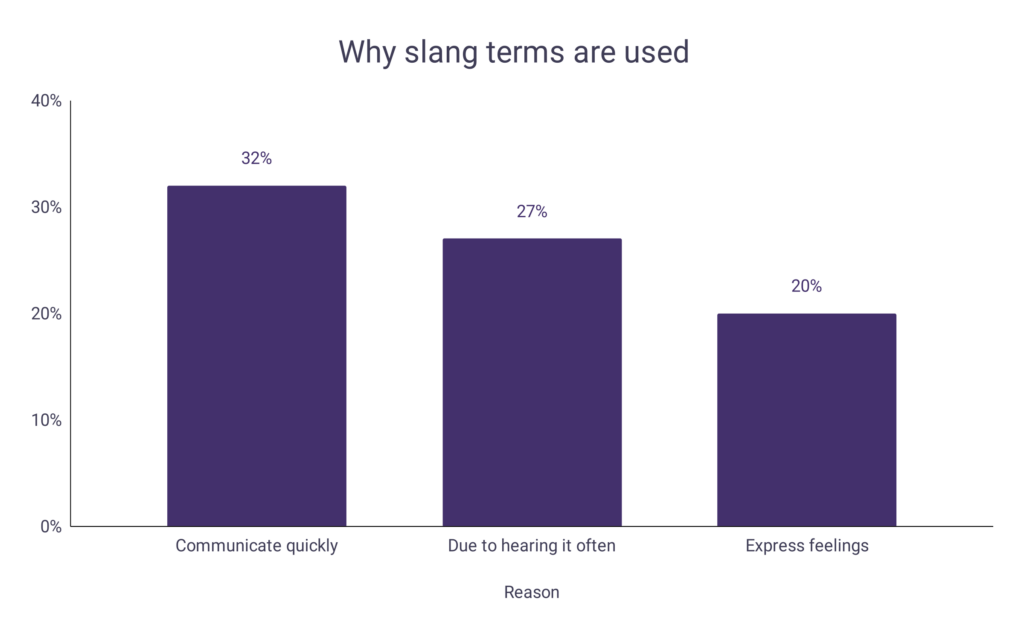
Why slang terms are used
Even though people use slang for a number of reasons, it typically allows us to communicate our thoughts and feelings with the listener at a much quicker rate, which is a key appeal for many people.
| Reason | Percentage |
| Communicate quickly | 32% |
| Due to hearing it often | 27% |
| Express feelings | 20% |
A graph is given below to show why slang terms are used:
Where slang terms are used
Slang terms have been around for a very long time, giving us plenty of time to evaluate and consider the best moments for their usage. As a general rule, the more formal the situation, the less likely people are to use slang. What’s more, people also appear to be more likely to use slang around people of their own age group.
| Situation | Percentage |
| With friends | 75% |
| With family | 64% |
| With partner | 44% |
| With coworkers | 28% |
| With strangers | 12% |
| With a boss | 10% |
A graph is given below to show where slang terms are used:

Acceptability of slang
In line with slang usage trends, people also tend to have common opinions on the correct and incorrect situations to use slang.
| Situation | Yes | No |
| Family event | 76% | 24% |
| In front of siblings | 83% | 17% |
| In front of parents | 69% | 31% |
| In front of grandparents | 59% | 41% |
| On a date | 69% | 31% |
| Professional setting | 46% | 54% |
A graph is given below to show the acceptability of slang:

Did you know, many Slang terms are even playable in a whole host of Word Games? If you are looking to play the best possible move for your next turn, check out the handy WordsRated Word Finder and watch your point score grow!
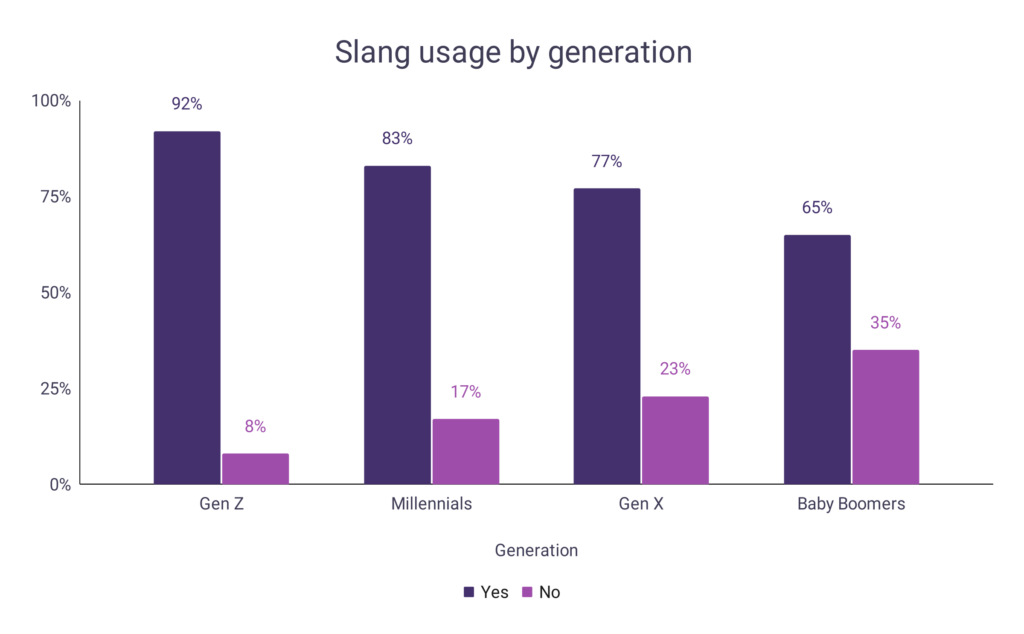
Slang usage by generation
Data shows that with each new generation, a higher percentage of people admit to using slang terms. This could potentially be linked to an increased use of technology and social media (where slang is prominent) in later generations.
| Generation | Yes | No |
| Gen Z | 92% | 8% |
| Millennials | 83% | 17% |
| Gen X | 77% | 23% |
| Baby Boomers | 65% | 35% |
A graph is given below to show slang usage by generation:
Opinions on people that use slang
When it comes to opinions on those that use it, slang is typically associated with a number of personal characteristics. Despite the vast majority of people using slang, there are still a number of prejudices associated with its usage.
| Opinion | Percentage |
| Person is young/youthful | 46% |
| Person is trying too hard | 34% |
| Person is cool | 11% |
| Person is lazy | 8% |
A graph is given below to show opinions on people that use slang:

What is slang?
- Slang is a type of language that is made up of informal words and/or phrases.
- When used, words/phrases are typically used within a particular context and shared between people that have similar backgrounds and interests.
- Overall, slang is much more commonly used in speech than in writing.
When was slang invented?
- The word “slang” was first recognized by Francis Grose (a lexicographer) in 1785.
- It was originally seen as a language used by the lowest-classes of people.
- Before slang was given its name, it was developed from a secret and cryptic language used by travelers, the homeless and criminals in England in the 1600s.
- This was used as a means of keeping information from other groups and authorities.
- In the early 1900s, it was typically associated with those that had a below-standard level of education in speech.
- Due to their nature, slang terms are often relatively short-lived when compared to other terms.
- However, slang terms are now commonplace and many are even accepted into dictionaries and word lists as standard language.
What are the types of slang?
One study attempted to group slang terms into the following five categories:
- Fresh and creative: Often, these are words we are already familiar with, and due to this we may not even notice them to be slang. They are a type of informal and clever vocabulary, where words can even be updated. Example: “Mommy” (Mother).
- Flippant: Multiple words that have no obvious connection to the new meaning they are applied to. Example: “Piece of cake” (easy).
- Imitative: Connects and borrows from multiple words to create a shortened term. These are frequently used when speaking but are much less frequent in writing. Example: “Gonna” (Going to).
- Acronym: Built from the first letters of words in a phrase and then pronounced as a word or as individual letters. Example: “OMG” (Oh my God).
- Clipping: Removes or replaces parts of an original term to create a shorter term that has the same meaning. Example: “Def” (Definitely).

