- The US publishing industry generated $29.33 billion in 2021, a 12.3% increase over the previous year.
- There were 825.7 million total US book units sold during Covid in 2021, an 8.9% increase over the previous year.
- US bookstores saw an 11.3% sales decline in 2020 compared with the previous year.
- However by October 2021, sales at bookstores were up nearly 40% compared to the same 2020 period.
- This was partly due to a greater adoption in online sales and the opening of new stores for both independents and chains.
- For the first time ever, online sales made up around 50% of trade sales.
- 71.4% of authors in the US reported drops in income since the start of the pandemic.
- Those who earned less lost 49% of their regular earnings on average.
- 24.5% of US authors applied for unemployment benefits or Covid-19 relief support schemes.
- Alongside Covid-19 itself and new supply chain issues, book distributors were affected by a high resignation rate from warehouse workers in the US.
- During 2020, 30% of people read more books or listened to more audiobooks than in previous years.
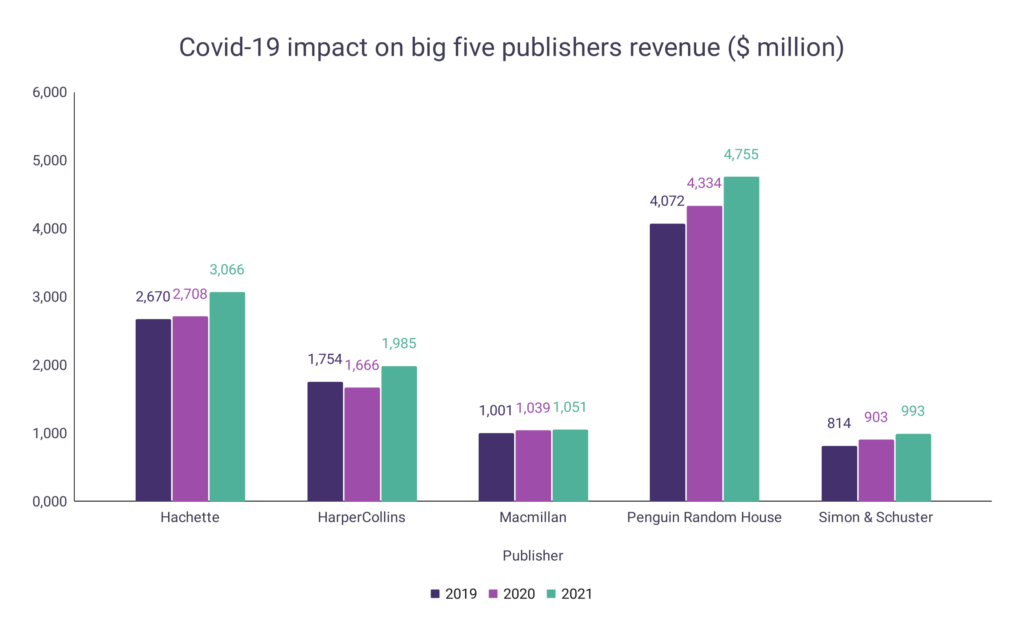
Covid-19 impact on big five publishers revenue
For the Big 5 publishing companies, total revenues increased over the three-year period from 2019 to 2021. Although the impact of Covid-19 was hard on many individuals and other businesses, the Big 5 continued to make revenue increases.
- Hachette’s revenue increased 14.83% to $3.07 billion over the period.
- HarperCollins’ revenue increased 13.17% to $1.99 billion over the period.
- However, the company did register a drop in revenue from 2019 – 2020, the only Big 5 publisher to do so.
- Macmillan’s revenue increased 5% to $1.05 billion over the period.
- Penguin Random House’s revenue increased 16.77% to $4.76 billion over the period.
- Simon & Schuster’s revenue increased 21.99% to $993 million over the period.
| Year | Hachette | HarperCollins | Macmillan | Penguin Random House | Simon & Schuster |
| 2021 | $3,066 | $1,985 | $1,051 (est.) | $4,755 | $993 |
| 2020 | $2,708 | $1,666 | $1,039 | $4,334 | $903 |
| 2019 | $2,670 | $1,754 | $1,001 | $4,072 | $814 |
A graph is given below to show the impact of Covid-19 on the revenue of the Big 5 publishers:
Covid-19 impact on educational publishing
During the Covid-19 pandemic, many schools, colleges and universities moved to online learning. Coinciding with this, educational publishers looked to embrace digital publishing, resulting in its major global market growth.
- US educational publishing grew by 15.2% during 2021 after dropping by 9% in 2020.
- The global digital educational publishing market is expected to grow 87.42% to $29.5 billion by 2027.
- Texts in digital educational material globally are expected to grow 114.72% to $11.38 billion by 2027.
- The global interactive textbooks market is expected to grow 16.5% to $2.3 billion by 2027.
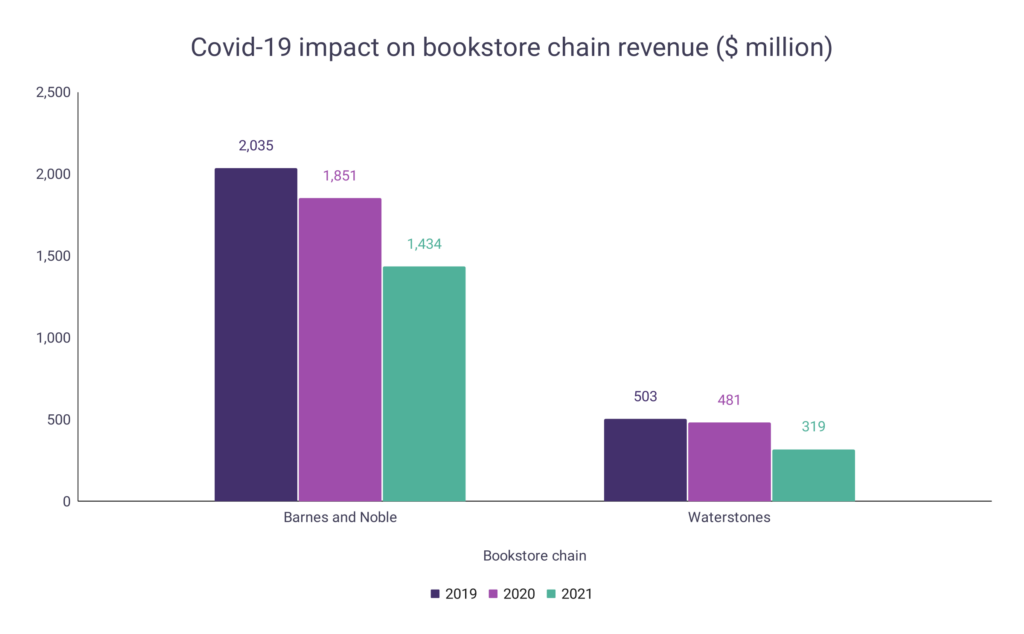
Covid-19 impact on bookstore chain revenue
The largest bookstore chains in the US and the UK however were hugely impacted by Covid-19. Health and safety measures such as increased social distancing implemented over the period greatly reduced in-store sales.
- Barnes and Noble’s revenue decreased 29.53% to $1.43 billion over the period.
- The company’s revenue dropped by $417 million in 2021 alone.
- Waterstones’ revenue decreased 36.58% to $319 million over the period.
- The company’s 2021 revenue was a drop of $162 million from the previous year.
| Year | Barnes and Noble | Waterstones |
| 2021 | $1,434 | $319 |
| 2020 | $1,851 | $481 |
| 2019 | $2,035 | $503 |
A graph is given below to show the impact of Covid-19 on the revenue of bookstore chains:
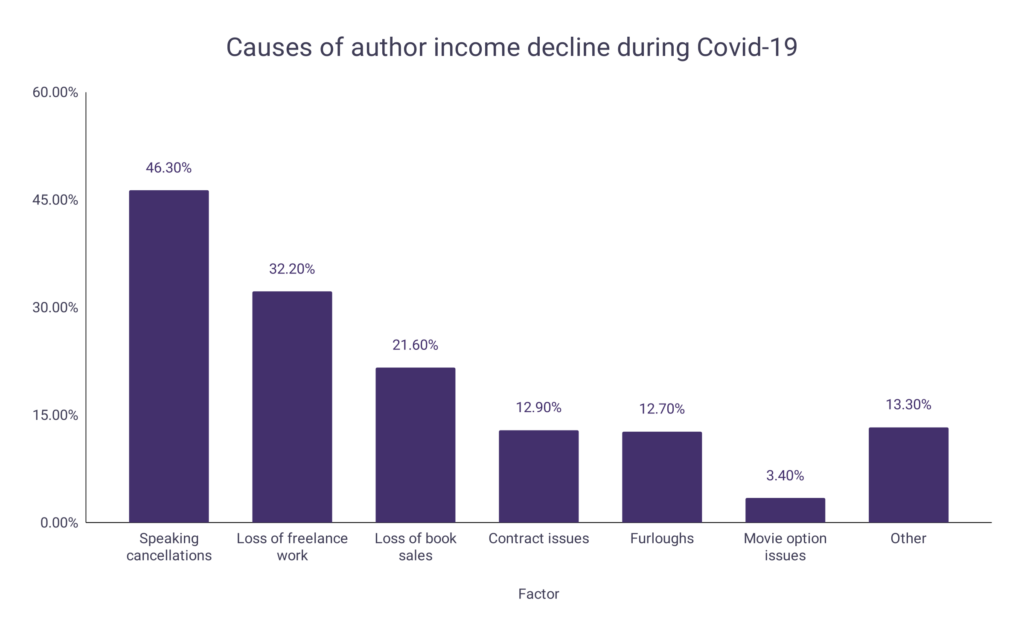
Covid-19 impact on author income
Authors also felt the financial effects of Covid-19, with the vast majority reporting that their income had fallen. Those that suffered drops in earnings found their income was almost halved, leading around 1 in 4 authors to apply for financial support schemes.
- The most common factor contributing to a drop in income for authors during Covid-19 was speaking cancellations (46.3%).
- 32.2% of authors with reduced incomes reported having a loss of freelance work.
- 21.6% of authors with reduced incomes reported having an overall drop in book sales.
- Contract problems, furloughs and issues with movie options made up the remaining factors.
| Factor | Percentage |
| Speaking cancellations | 46.3% |
| Loss of freelance work | 32.2% |
| Loss of book sales | 21.6% |
| Contract issues | 12.9% |
| Furloughs | 12.7% |
| Movie option issues | 3.4% |
| Other | 13.3% |
A graph is given below to show the causes of author income declines during Covid-19:
Covid-19 impact on book publishing industry events
- During 2020, author tours, conferences and fairs became hosted virtually as an industry standard practice to reduce the spread of Covid.
- Although there was a hope for these events to return to in-person attendance during 2021, most events continued in a virtual format at the start of the year.
- Bookstores began hosting live author appearances (outside or indoor with limited masked attendances) during the summer months.
- However, towards the winter new variants continued to appear, affecting the continuation of in-person events.
Covid-19 impact on the book publishing supply chain
The pandemic contributed to major supply chain problems across almost all industries, especially those with a dependence on overseas sellers. Book publishing was no exception and had to respond quickly by implementing a range of new measures.
Causes of supply chain problems
- In US book publishing and manufacturing, shortages of truck drivers, congested ports and high freight container prices made it difficult for the industry to deliver books in time, especially over the festive season.
- Furthermore, companies with large warehouses, such as Amazon and Ingram, suffered from widespread shortages of labor.
- Companies struggled to find skilled workers whilst simultaneously dealing with ongoing paper shortages, resulting in printing capacity issues.
Solutions to supply chain problems
- To counter these problems, publishers looked to focus on delivering frontlist titles on time, delaying their other releases.
- Publishers also looked to move more printing back to the US and encouraged a higher use of print-on-demand services.
- The development and further implementation of technology and automation are believed to be the best long-term solutions to address supply chain issues by experts in the industry.

